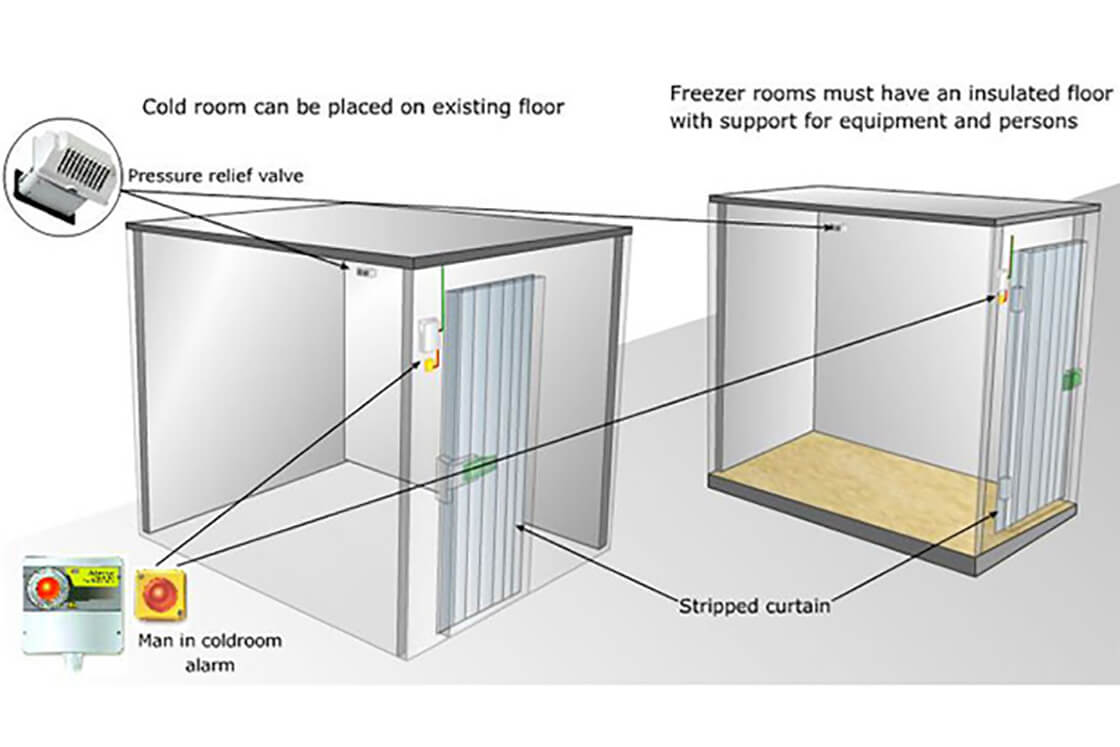
In this second part of ‘What you need to know about refrigeration’ we will deal with the construction of a suitable cold storage room. We will concentrate on the practical challenges and requirements for setting up such an environment.
Thermostatic or electronic expansion valves

Simple refrigeration circuits can be used for cold storage rooms. Simple refrigeration circuits are cost-effective and not complicated, however, they do have some disadvantages, for example, the risk that stored products, which are not packed or covered, will dry out. Thermostatic expansion valves are installed as injection valves in most cold storage rooms. An electronic super-heat controller offers several advantages for anyone who might be looking for a better solution. The evaporator should be always filled with refrigerant for optimal use. Even in the event of strong capacity fluctuations (that is, part-loads), the amount of refrigerant, which is to be injected, can be dosed accurately. This is done by promptly transmitting the current superheat in the evaporator - using a pressure transmitter and a very sensitive temperature sensor - to the electronic controller - the controller can now take action to control the optimum amount of superheat in the evaporator to ensure the best operation of the system. This adaptive regulation of the refrigerant injecting leads to optimal use of the evaporator and thereby, to the highest possible evaporation pressures which are feasible in this specific plant. However, this not only means a reduced electricity bill for the user - due to the lower temperature differences between the evaporation and room temperature, there is a reduced dehumidify of air in the room and with it less dry out of the refrigerated goods. The same configuration means that, for example, vegetables, which are stored in a room with an evaporator with electronic expansion valve regulation, remain visually presentable and fit for sale for a longer period than with thermostatic expansion valves. Furthermore, the refrigerated goods dry out less. If the design of the evaporator is somewhat too small, a larger evaporator allows you improve the conditions even further with the effects "higher evaporation temperature" and "less de-humidification".

Defrosting
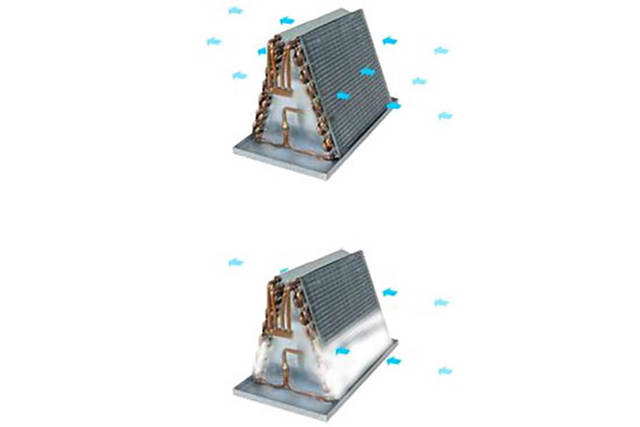
Frost will build up on the surface of an evaporator if its temperature is at or below 0°C. Frost which builds up on the evaporator can arise in different forms, that is as snow (powdery snow or snowflakes), as solid ice or in any other intermediate form respectively.
Frost is caused by the withdrawal of water from the goods as well as from the atmospheric humidity (air which flows through the air cooler). Defrosting is understood as the removal of frost which has built up on the surface of the evaporator.
Defrosting can help prevent the excessive built up of frost on the refrigeration surfaces, which reflects in a good heat transfer and an optimal operation of the plant. Moreover, regular defrosting brings about an unobstructed circulation of air, whereby the air cooler performance improves.
How often, and the length of time for which defrosting is carried out is dependent on, among other things, the stored products, and their moisture content as well as air exchange and humidity. How many times a day the door to the cold storage door is opened or somebody enters the room also plays a major role. The cold storage room needs to be defrosted as often as required and above all in a timely manner. If the defrosting period is too short and not all the ice melts, then even more ice will build up with time.

The type of defrosting is just as important as the defrosting time/frequency. There are three customary defrosting methods. Air circulation (thawing out in the cold storage room), electric, and hot gas defrosting. Natural defrosting (air circulation) with the help of air is possible if the temperature in the cold storage room is higher than +4°C. Cooling of the cold storage room is stopped but the fan continues to run. This process can take longer than the other defrosting methods, however, defrosting can also be sped up by increasing the temperature. This process is energetically advantageous since no additional heat is produced, which must be removed from the cold storage room again later.
Electric defrosting is the most common and at the same time a simple defrosting method for cold storage rooms. The evaporator just must be installed with electric heaters and connected to electrical cables. This tends to be a more expensive defrosting method from an energy point of view because it uses a lot of energy. On the other hand, electric defrosting can be well controlled and represents perhaps the only feasible defrosting option. Defrosting can be started using a real-time clock, time intervals or manually and ended according to a pre-set temperature or after a certain period of time.
The third defrosting method, namely hot gas defrosting, involves gas being diverted from the high-pressure side of the refrigeration plant to be used for the defrosting. In principle, energy is saved through the hot gas defrosting method. However hot gas defrosting is a relatively complicated defrosting method and is mainly used in large plants with several evaporators. Evaporators can be operated at the same time as other evaporators are defrosted, thus defrosting alternately. More valves are required for hot gas defrosting and the control system is also more complicated than both other common defrosting methods. When hot gas defrosting, it is highly recommended that a liquid separator is built in, to protect the compressor from liquid return. A pressure regulator can also protect the compressor from high suction pressure. Cold gas defrosting can also be an alternative to hot gas defrost. This simply involves extracting the high-pressure refrigerant from the top of the receiver instead of directly out of the hot gas line.
However, it's not only the defrosting method that is important; energy costs can be reduced by skipping a defrosting operation, especially if it isn't needed. Skipping every fifth defrosting process is already a huge energetic advantage. It's very important that the plant is only defrosted at the programmed times. If this is not the case, then defrosting could be started at unfavorable times (e.g., when awaiting delivery of goods). Fitting a refrigeration controller with defrost on demand can be positively reflected, by itself, in the end user's electricity bill.
Conclusion
There are certain points that must be taken into consideration when designing, assembling, and using cold storage rooms - we learnt more about this in these two editions of "What you need to know about refrigeration". Careful commissioning and regular maintenance ensure that the plant runs smoothly, and that energy is not wasted unnecessarily. Energy improvements are also possible for existing plants by fitting electronic expansion valves and refrigeration regulators for defrost on demand.