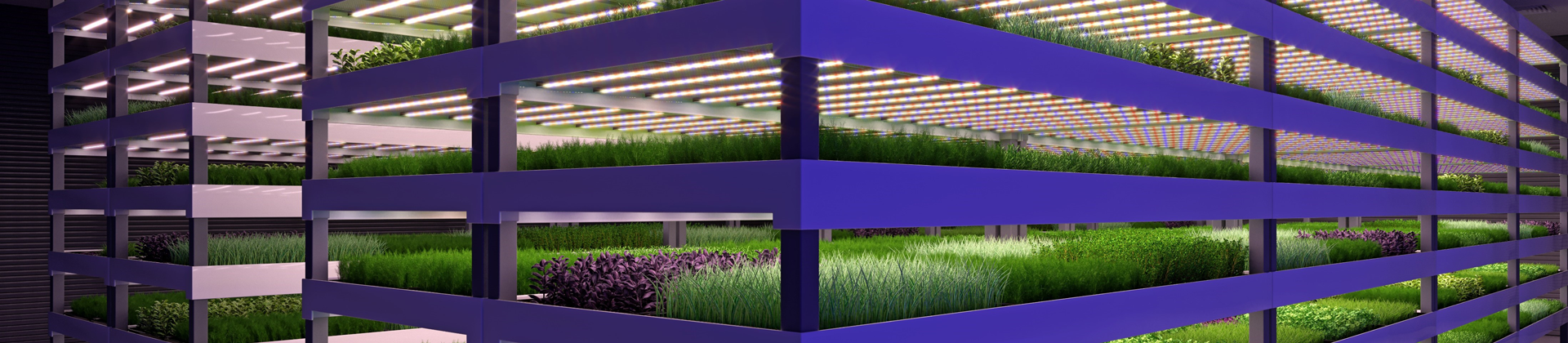
Vertical Farming
We’re here to help you boost your vertical farm’s energy efficiency and create the optimal growth conditions for your crops.
Get in touch with us
Energy efficient vertical farming
Vertical farming and controlled environment agriculture will play an important role in increasing food production globally. But a vertical farm is also a heavy energy consumer. We’re here to make vertical farming more energy efficient. Our comprehensive technology portfolio addresses everything from climate control to water circulation and nutrient distribution, and can help you cut your vertical farm’s energy use.
Why do we need vertical farming?
By 2050, the world must boost food production by 70%* to meet the needs of an ever-growing population. However, we’re already using most of the arable land available for traditional farming. At the same time, traditional agricultural production is under pressure by climate change, water scarcity and urbanization. To solve these challenges, we need to find innovative ways of growing food, and develop solutions that support urban farms and agriculture. That’s where vertical farming comes into the picture.
Vertical farming stacks crops vertically in indoor environments, using artificial lighting and precise climate control to create optimal growth conditions. This makes it possible to grow fruits, vegetables, and herbs in an urban environment where traditional soil-based systems would be infeasible.
* UN Report on Sustainable Food Production
Advantages of indoor farming
The advantages of vertical farming include using less water and enabling year-round local production, higher yield per m2, and healthier crops.
Indoor farming uses 95% less water than traditional farming. Water is saved by applying precision irrigation techniques to deliver water directly to the roots, and only when it is needed by the plants. Furthermore, water is recirculated in a closed loop, avoiding any water waste.

By stacking crops vertically on top of each other, vertical farms can produce a much higher yield per m2 than traditional farming.

Because crops are cultivated indoors in a fully controlled environment, vertical farms enable year-round production of usually seasonal crops in any climate. This reduces the dependency on importing fruits and vegetables during off-season periods, minimizing the carbon footprint.

By Growing crops in fully closed and controlled environments there is no need for using any pesticides. And with the precise control of growth conditions, you can produce healthier crops with high protein and nutrition levels.

Vertical farmers can produce food closer to urban consumers, reducing food waste by increasing shelf life, and cutting down on transport costs and emissions in the process.
We make vertical farming more energy efficient
Yet, there are challenges. To create optimal growing conditions, vertical farmers use artificial LED lighting. These lights create heat, and the plants create humidity, meaning indoor farms need both cooling and dehumidification systems to maintain the right climate for crop growth. All of this requires a significant amount of energy. In fact, up to 40% of a vertical farm’s energy consumption comes from heating and ventilation.
These farms need to be able to compete with traditional field- or greenhouse-grown produce, from local and imported sources, and maintain a sustainable business model.
Danfoss offers energy-efficient technologies to apply in climate control solutions and in water circulation for irrigation and hydroponic systems. For example, our technologies can help cut energy usage in heating and ventilation (HVAC) systems by up to 30%. We work with commercial indoor farms to make food production more energy efficient and create a sustainable future for indoor farming.
FAQ
Vertical Farming FAQ
What is vertical farming?
Vertical Farming or indoor agriculture is a technology-based approach to growing crops indoors. This allows growers to specify and control the ideal environment to achieve the optimal harvest. Growers can do this by controlling temperature, humidity, airflow, CO2 levels, lighting, irrigation and fertilization.
What do I need to consider if I want to build a vertical farm?
Starting a vertical farm requires careful planning and consideration of various factors. Here are some key aspects to think about:
- Location: Decide where you want to set up your vertical farm. Consider factors such as available space, access to utilities like water and electricity, proximity to markets or consumers and zoning regulations.
- System: Choose the type of farming system that best suits your needs and resources. Options include hydroponic farming, aeroponic systems, aquaponic systems and stacked shelving systems. Each has its own advantages and requirements in terms of space, cost and complexity.
- Crop Selection: Determine which crops you want to grow based on market demand, climate suitability and your own expertise. Leafy greens, herbs, microgreens, strawberries, and certain vine crops are popular choices for vertical farming due to their compact growth habits and high value.
- Infrastructure and equipment: Invest in the necessary infrastructure and equipment for your farm, including growing containers or systems, lighting fixtures, environmental controls (e.g., HVAC systems), irrigation systems and monitoring equipment. Consider both upfront costs and ongoing operational expenses.
- Lighting: Choose appropriate lighting, especially if you're growing indoors or in low-light environments. LED grow lights are commonly used in vertical farming due to their energy efficiency, customizable spectra and ability to mimic natural sunlight.
- Environmental controls: Implement systems to regulate environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, ventilation and CO2 levels. Maintaining optimal growing conditions is crucial for maximizing crop yields and quality.
- Water and nutrient management: Develop a water and nutrient management plan to ensure that your plants receive essential nutrients and hydration. Depending on your chosen growing system, you may need to use a hydroponic nutrient solution, aeroponic misting system or aquaponic fish waste to fertilize your crops.
- Labor and maintenance: Consider the labor requirements for operating your farm, including planting, harvesting, pruning, pest management and system maintenance. Determine whether you'll need to hire additional staff or if you can manage the workload yourself.
- Regulatory compliance: Familiarize yourself with local regulations and permits related to agriculture, food safety, building codes and business licensing. Ensure your farm complies with all relevant laws and regulations.
- Market research and business plan: Conduct market research to assess demand for your chosen crops and identify potential customers or distribution channels. Develop a detailed business plan outlining your goals, target market, marketing strategies, financial projections and risk management strategies.
- Sustainability: Consider your farm’s environmental impact and explore ways to minimize resource consumption, waste generation and carbon emissions. Sustainable practices such as water recycling, energy efficiency, and organic cultivation methods can enhance the long-term viability of your operation.
How do I choose the right HVAC system?
Since heating and ventilation account for 40% of a vertical farm’s energy consumption, choosing energy-efficient HVAC equipment can go a long way in reducing your farm’s operating expenses. It’s also important to choose a system that will give you precise control over temperature, CO2 levels, humidity and heat loads.
What is Hydroponic farming?
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants in a soilless medium while providing all the necessary nutrients directly to the plant roots. A hydroponic system consumes up to 90% less water than traditional field crop watering methods because most hydroponics systems use recirculation techniques to minimize waste.
To help hydroponic plants grow, farmers need to maintain the correct nutrient balance by using nutrient rich water that circulates directly around the plant’s roots. This is done using specially developed irrigation systems.
What is Urban farming?
Urban farming refers to the practice of cultivating, processing, and distributing food in or around urban areas. It encompasses a variety of agricultural practices, including growing crops, raising livestock, and aquaculture, all within city limits or nearby urban environments. Urban farming can take place in diverse locations such as rooftops, vacant lots, community gardens, and even indoor spaces like warehouses and shipping containers.
The goals of urban farming typically include increasing local food production, promoting food security, reducing food miles and carbon emissions associated with transportation, utilizing underutilized urban spaces, fostering community engagement, and enhancing urban greenery.
What is Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA)?
Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) refers to a farming method where various environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, light, and nutrient levels are precisely controlled within a closed or semi-closed system. This allows for the cultivation of crops in environments that may be otherwise unsuitable for traditional agriculture, such as arid regions or urban areas. CEA often involves the use of technologies like hydroponics, aeroponics, aquaponics and vertical farming systems to optimize resource usage and crop growth. By tightly regulating the growing conditions, CEA aims to maximize yields, minimize resource consumption and produce high-quality crops year-round.
Contact us
Find out how our technologies can make your farming operation more energy efficient.
Get in touch here.


