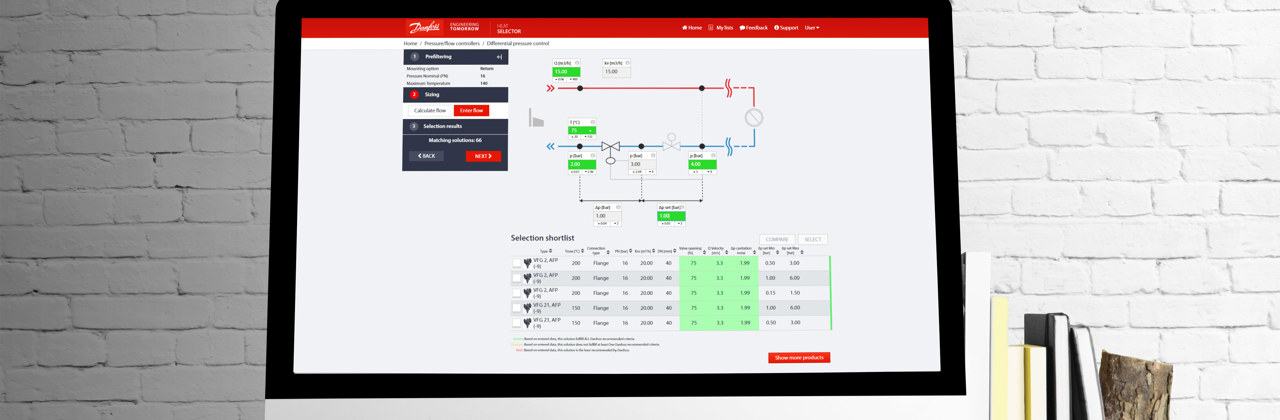
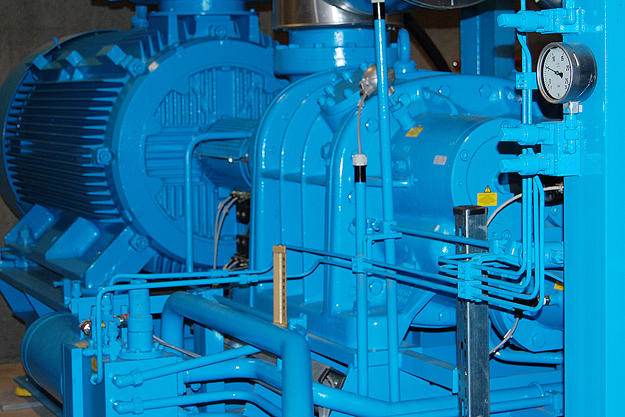
By means of a flexible and modular design, it is possible to combine several control functions into one controller to meet the most demanding requirements across a wide range of applications.
In some applications, it may be necessary to control the flow temperature, limit maximum flow rate and primary return temperature by using a single multifunctional controller.
A typical example of such a device is the AVQMT, which works like the AVQM but with an additional self-acting thermostat (type AVT / STM).
The pressure-independent valve controls the temperature on the secondary side and the self-acting thermostat limits the return temperature. In domestic hot water systems, the thermostat can be used as a safety thermostat protecting users from scalding.
Features and benefits
Eliminates pressure variations and provides optimum operating conditions with improved temperature control quality
Made for demanding systems, resistant to corrosion, cavitation and dirt
Connected system is protected against pressure surges, fluctuations, cavitation and noise
Differential pressure and flow controllers in district heating or cooling systems (variable flow)
Balance your network, save energy and improve end user comfort by hydronic balancing and control of district energy networks.
Tools and apps
FAQ
Case studies
-
if (isSmallPicture) {


 Danfoss partners with the city of Banja Luka to decarbonize district energy
Danfoss partners with the city of Banja Luka to decarbonize district energyThe Challenge: Renovate 34 of the city’s largest heating substations
The Solution: Danfoss Leanheat® Monitor enables full substation digitalization
The Results: reduced heat consumption by 10% -
if (isSmallPicture) {


 Successful transition from oil boilers to a local heating network in Eurasburg
Successful transition from oil boilers to a local heating network in EurasburgIn the Wittelsbacher Land near Augsburg the local network in Eurasburg supplies heat to 80 buildings using a wood chip heating system. Danfoss’ substations ensure efficient heating in all building types, and its modern SCADA solution enables remote system monitoring and management.
-
if (isSmallPicture) {


 Intelligent optimisation of district energy in new residential apartments
Intelligent optimisation of district energy in new residential apartmentsTwo new build apartments in Docklands, London and Newbury Racecourse, Berkshire have been equipped with intelligent Danfoss solutions, bringing increased control and stability as well as greater than 20% peak energy reduction.
-
if (isSmallPicture) {


 Leanheat makes buildings smart
Leanheat makes buildings smartIn Europe, 30 percent of all energy consumption goes to heat or cool buildings. Danfoss has the solution to lower energy usage and improve indoor climate by adding a digital element: Leanheat software.
-
if (isSmallPicture) {


 A cost-effective solution: district cooling in central Copenhagen
A cost-effective solution: district cooling in central CopenhagenEnergy efficiency was a major consideration in the design of Copenhagen’s district cooling project, where VLT® drives contribute to reducing CO2 emissions by more than 3000 t annually.
-
if (isSmallPicture) {


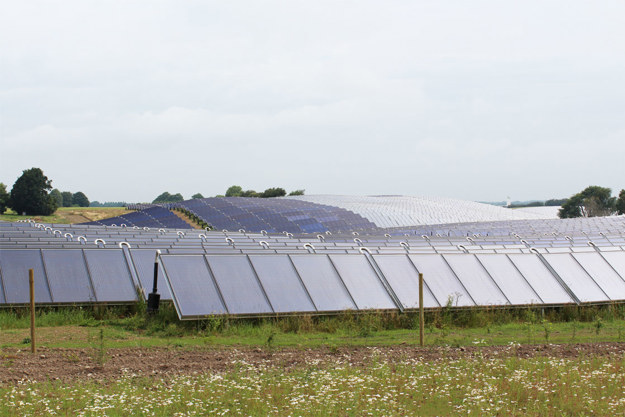
 Solar heating plant reduces CO2 emissions by 15,700 tonnes annually
Solar heating plant reduces CO2 emissions by 15,700 tonnes annuallyThe world’s largest solar heating plant in Silkeborg, Denmark harnesses energy to heat the homes and workplaces of 40,000 citizens. It supplies 18-20% of the annual heat consumption in the city of Silkeborg, Denmark, which has an ambitious target of CO2 neutrality in heat production by the year 2030.